MIL-B-49030A
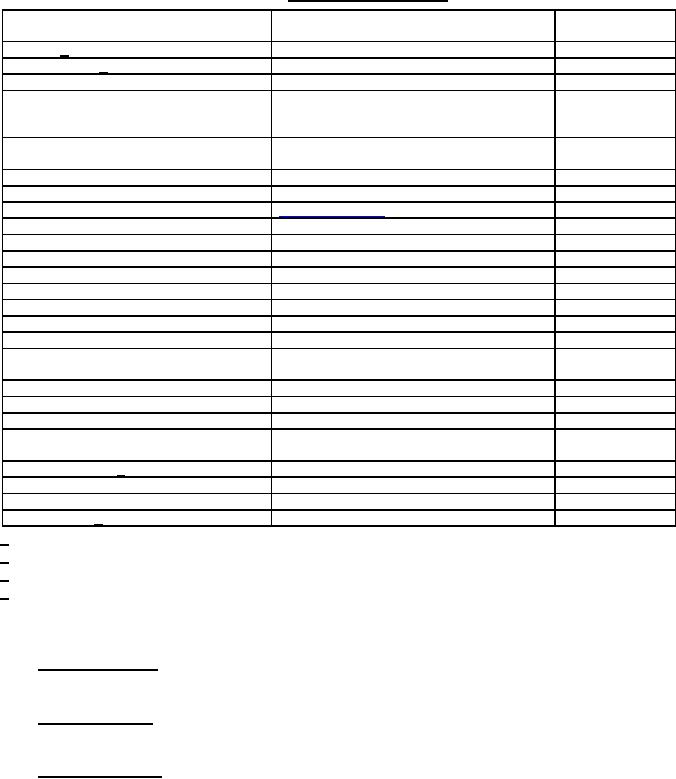
TABLE I. Materials and components.
Materials and components
Applicable specifications or requirements
Methods of test
(see 4.4)
(see 4.4.1)
Solder 1/
Soldering flux 2/
J STD-004, J STD-005 and J STD 006
Metals
Brass
Copper
Beryllium copper
Phosphor bronze
Terneplate
Nickel plating
Wire
Machine screws, studs, and nuts
Plastic, laminated
ASTM D709, type PBE
Plastic, molded
Plastic polyethylene
Webbing, cotton
Tape
Insulating, impregnating, potting, and
sealing compounds
Filler or padding
Cell-block-container material
Intercell separation
Terminals
4.7.4.1.1 and
Jackets, metallic 3/
Jackets, nonmetallic
Terminal mounting plate
Strap handle 4/
1/
For electrical connections, type Sn40 or higher tin content shall be used.
2/
If other fluxes are used, they shall not affect the performance of the battery or reduce its shelf life.
3/
Test method 4.7.2 is applicable only for metallic jackets of material other than terneplate.
4/
Applicable to batteries with metallic jackets only.
3.5.4 Cell-block container. Cell-block container shall be an insulating material surrounding a group or a stack of
individual cells.
3.5.5 Intercell separation. A separator shall be placed between cells in series connected multicell batteries. The
separator shall be an insulating material.
3.5.6 Intercell connections. Intercell connections shall be spot welded in accordance with AWS D17.2/D17.2M,
class B, or soldered depending upon the applicable terminal. Connections between cell blocks and between cell
block and terminal shall be so insulated or positioned as to avoid contact with other conducting material or jacket of
the battery. When insulated wire is soldered to terminal lugs, it shall not be bared more than .094 inch (2.39 mm)
from the lug nor shall it extend more than .094 inch (2.39 mm) beyond the lug.
5
For Parts Inquires submit RFQ to Parts Hangar, Inc.
© Copyright 2015 Integrated Publishing, Inc.
A Service Disabled Veteran Owned Small Business